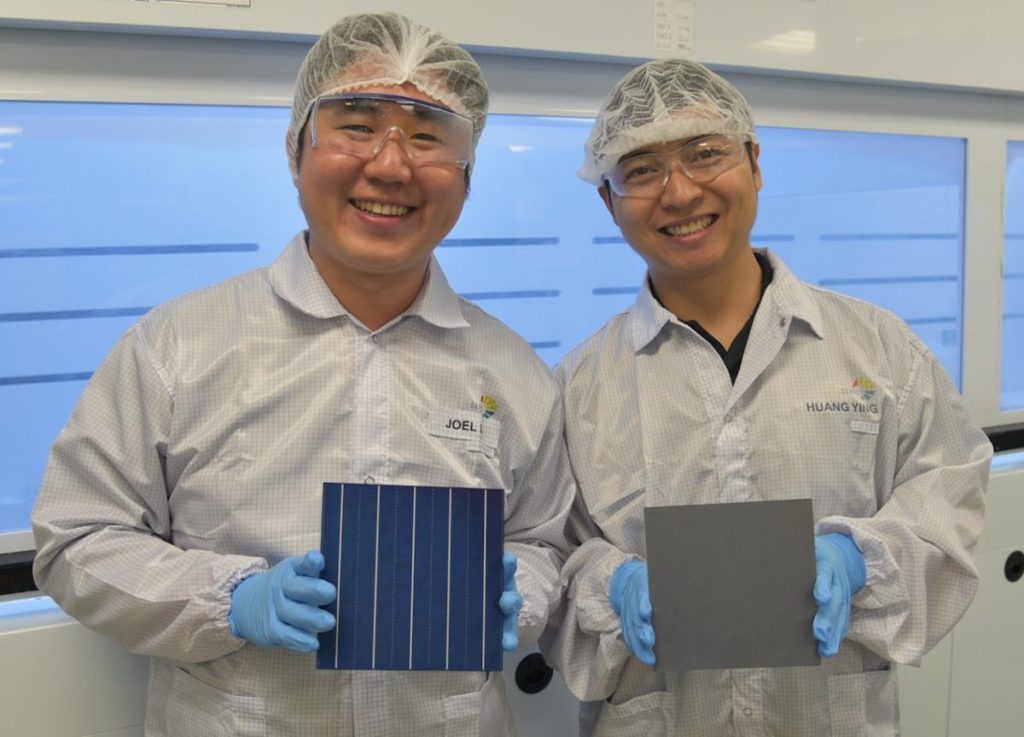
新加坡太阳能研究所(SERIS)的科学家们开发出一种新型湿化学方法,能利用金刚石绳锯技术切割多晶硅片,并随后织构以降低反射率。
这一湿化学法以纳米特征尺度刻蚀晶片表面,从而增加了光线反射表面的次数及被晶片材料吸收的机会。该工艺使用专利性化学品,具有低成本性和可扩展性,且极易被集成入电池生产线。
SERIS认为,相较于“黑硅”工艺,其新工艺能给生产厂家提供更多的益处。表示他们的技术“更简单、更价廉,且无金属,可以达到20%以上的电池效率”,有潜力成为被多晶硅太阳能电池制造商广泛使用的主流织构技术。
据SERIS表示,这一工艺已获得了几家一线厂商的认可。该机构准备与这些厂家密切合作,将其扩大到大型生产线。
This content is protected by copyright and may not be reused. If you want to cooperate with us and would like to reuse some of our content, please contact: editors@pv-magazine.com.













By submitting this form you agree to pv magazine using your data for the purposes of publishing your comment.
Your personal data will only be disclosed or otherwise transmitted to third parties for the purposes of spam filtering or if this is necessary for technical maintenance of the website. Any other transfer to third parties will not take place unless this is justified on the basis of applicable data protection regulations or if pv magazine is legally obliged to do so.
You may revoke this consent at any time with effect for the future, in which case your personal data will be deleted immediately. Otherwise, your data will be deleted if pv magazine has processed your request or the purpose of data storage is fulfilled.
Further information on data privacy can be found in our Data Protection Policy.