来自亥姆霍兹柏林材料与能源研究中心(HZB)、剑桥大学、加州理工大学(Caltech)、伊尔梅瑙理工大学(TU Ilmenau)和弗劳恩霍夫太阳能系统研究所(Fraunhofer ISE)的一个联合研究团队,最近展示了他们开发的新型太阳能水分离电池,其效率可达19.3%。
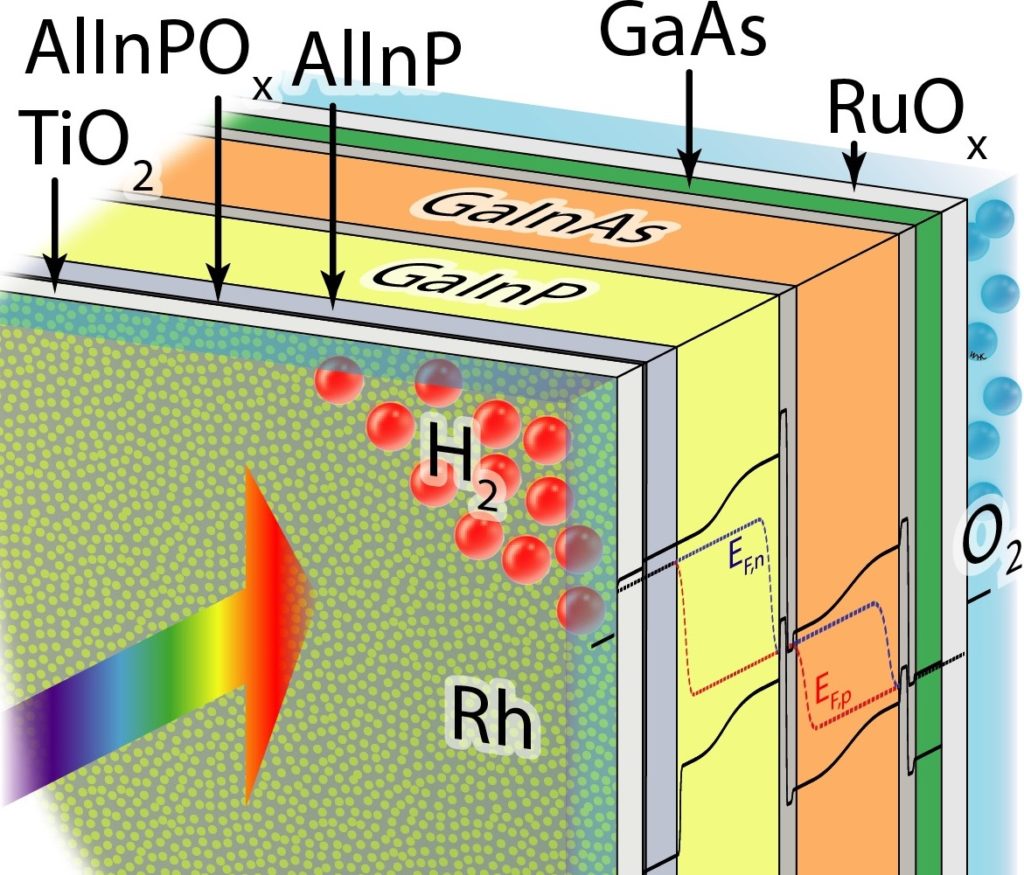
研究人员表示III-V族半导体的串联太阳能电池与铑纳米颗粒及结晶二氧化钛催化剂的组合推动了效率的提高,声称通过将电池浸入水介质中,电池可直接用于从水中形成氢,并解释说太阳能电池与催化剂的组合以及单片光电极简化了水的分裂。研究团队的Matthias May博士表示,晶体二氧化钛层不仅保护了实际的太阳能电池免受腐蚀,而且还提高了电荷传输。他们已经可以将电池的使用寿命延长到100小时左右,这是一个重大的进步。
Fraunhofer ISE 所提供的高效串联电池,让研究团队得以降低电池的表面反射率,而这也是新电池技术的创新所在。晶体二氧化钛层代替了防腐顶层,它不仅具有优异的抗反射性能,而且催化剂颗粒也能附着于其中。
此外研究人员还使用了一种新的电化学方法来生产铑纳米颗粒,用于催化水裂解反应。这些粒子的直径只有十纳米,因此在光学上几乎是透明的,使它们成为非常理想的材料。
该团队强调了利用可再生能源生产氢气的重要性。迄今为止,可再生能源制氢的效率相对较低。能够直接分裂水的更高效电池可能成为克服这一障碍的一种方法。
本文作者:MARIAN WILLUHN
This content is protected by copyright and may not be reused. If you want to cooperate with us and would like to reuse some of our content, please contact: editors@pv-magazine.com.












By submitting this form you agree to pv magazine using your data for the purposes of publishing your comment.
Your personal data will only be disclosed or otherwise transmitted to third parties for the purposes of spam filtering or if this is necessary for technical maintenance of the website. Any other transfer to third parties will not take place unless this is justified on the basis of applicable data protection regulations or if pv magazine is legally obliged to do so.
You may revoke this consent at any time with effect for the future, in which case your personal data will be deleted immediately. Otherwise, your data will be deleted if pv magazine has processed your request or the purpose of data storage is fulfilled.
Further information on data privacy can be found in our Data Protection Policy.