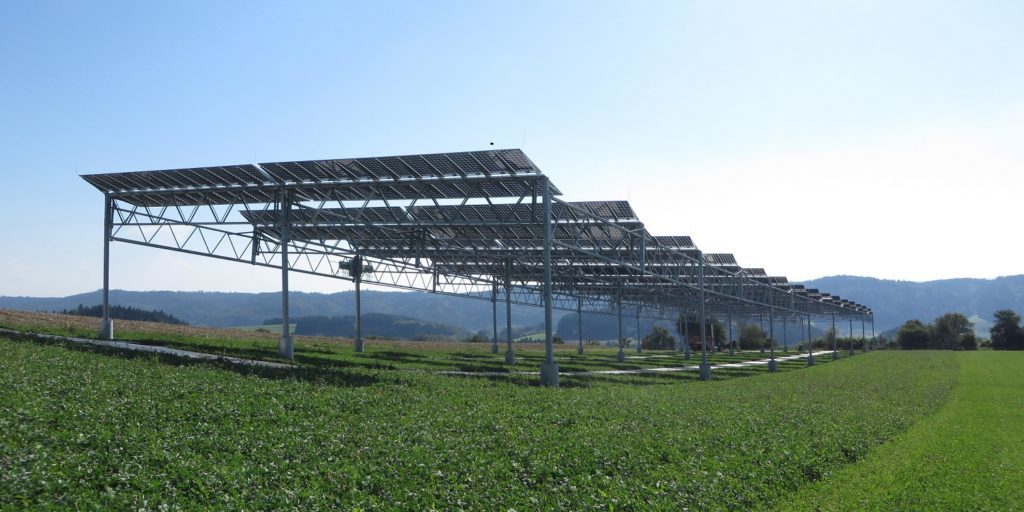
德国太阳能研究所Fraunhofer ISE的研究证明,将太阳能发电与农业活动相结合,不仅可以降低成本、显著提高土地利用效率,而且还特别适用于干旱地区。
该研究所在康斯坦斯湖附近的一个194千瓦农用光伏试验装置,得益于破纪录的晴朗夏季,去年每公顷土地利用率上升了186%,而去年同期的增长率为160%。
研究人员表示,太阳辐射的增加,是太阳能发电量增加的原因。而光伏电池板下的太阳辐射减少了30%,它与较低的土壤温度和降水分布相结合,对土地利用效率的上升起到了促进作用。“半透明太阳能组件下的阴影,使这些植物能够更好地经受2018年的炎热和干燥条件。”并补充说对于降雨量很少的地区,农业光伏发电是一个良好的选择。
Fraunhofer-ISE的专家们认为,由于规模经济和学习效应,农业光伏装置的成本将会进一步下降,而且它们已经与小型屋顶太阳能系统成本相当。除此之外,耕地上的光伏系统所有者还可以从能源储存或农用电动汽车使用的增加中获得额外的收入来源。
该机构目前正在开发一系列项目,以便将这项技术转让给发展中国家,并对其进行其他方面的应用测试。
This content is protected by copyright and may not be reused. If you want to cooperate with us and would like to reuse some of our content, please contact: editors@pv-magazine.com.












By submitting this form you agree to pv magazine using your data for the purposes of publishing your comment.
Your personal data will only be disclosed or otherwise transmitted to third parties for the purposes of spam filtering or if this is necessary for technical maintenance of the website. Any other transfer to third parties will not take place unless this is justified on the basis of applicable data protection regulations or if pv magazine is legally obliged to do so.
You may revoke this consent at any time with effect for the future, in which case your personal data will be deleted immediately. Otherwise, your data will be deleted if pv magazine has processed your request or the purpose of data storage is fulfilled.
Further information on data privacy can be found in our Data Protection Policy.